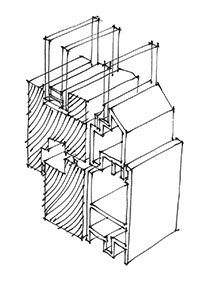
Dictionary
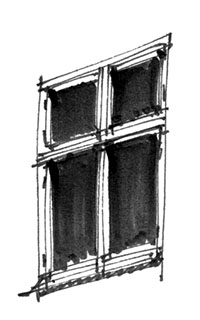
Casement window
A window that opens on hinges like a door. With a closing mechanism (fastener).
A four-light casement window, the outline of which may be compared to the Danish flag “Dannebrog”: The two lower casements are about twice the height of the top sashes. Mullion and transom forms a cross, and the window is usually called a “cross window”. The window is common in residential houses from the 18th and 19th centuries. Also short form ‘casement’.
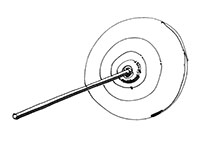
Crown glass
Early type of window glass, also called moon glass. In the process, glass was blown into a "crown" or hollow globe. It was then flattened by reheating and spinning out the bowl-shaped piece of glass (bullion) into a flat disk by centrifugal force. The glass was then cut to the size required.
Known as bull’s eye (or Oeil de Boeuf), the centre area, which was thicker than the rest, was used for less expensive windows.
Cudo
Double glazed insulating pane (DGU), where the edge sealant fits tightly to the edge of the glass sheets. The air spacer bar is made of lead and filled with a humidifier. The spacer is soldered on to both glass units using lead. The insulating pane was marketed under the name Cudo. Today referred to as an “old fashion DGU”.
Cylinder glass
A type of glass made by a method developed about 1100. A glass blowing pipe with a lump of glass is swung over a large trench while rotating. The lump is blown into a cylindrical iron mould. The ends are cut off and a cut is made down the side of the cylinder. The cut cylinder is then placed in an oven where the cylinder unrolls into a flat glass sheet.