Dictionary
Window
The word originates from the Old Norse ‘vindauga. ‘Vind’ meant roof - where the earliest windows were placed - and ‘auga’– meant eye or opening. A window is an opening that allows the passage of daylight into a building. By opening and closing the window you ensure a good air change and you can control the temperature in the room. The window also provides a view out and contact with the surrounding area. In special cases it also works as a fire escape window or rescue exit. Through history the window has had many shapes defined by capacity of craftsmen and technology, performance and energy demands and aesthetic ideals.
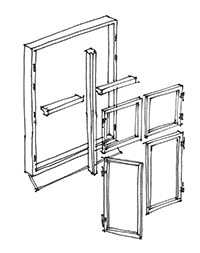
Usually a window is composed of a top frame, two side pieces and a bottom frame/sill. The opening may be divided up by transom and mullion. Between those are the sashes or casements, which again can be divided up by muntin/glazing bars keeping the panes in place. For several millenniums houses have had embrasures, however, in Europe the first windows with panes were introduced around 1100.